Two-samples t-Tests: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
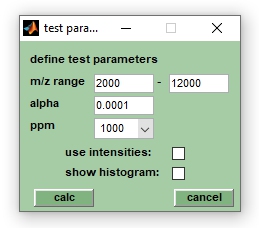
[[File:T-test.jpg|right| | [[File:T-test.jpg|right|thumb|Input parameters for univariate t-tests]] | ||
This function performs two-samples t-tests in each segment of the MALDI- | This function performs two-samples t-tests in each segment of the MALDI-ToF mass spectra using peak table data as inputs. t-tests are useful for biomarker screening in ensembles of mass spectra exhibiting certain degree of similarity. A two-samples t-test in a given m/z segment returns a test decision for the null hypothesis H(0) that the peak intensity data in class I and class II come from independent random samples from normal distributions with equal means and variances. The alternative hypothesis H(1) is that the peak intensity data come from populations with unequal means. | ||
See also [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student's_t-test| t-test] (Wikipedia) | See also [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student's_t-test| t-test] (Wikipedia) | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* m/z range: boundaries of the m/z region in which the t-tests are performed | * m/z range: boundaries of the m/z region in which the t-tests are performed | ||
* α: significance level of the t-tests | * α: significance level of the t-tests | ||
* dx (ppm): a parameter defining the width and the number of the m/z spectra segments. For example, a spectral segment centered at the position x covers a m/z interval of the width x * dx/10^6. The boundaries of the spectra segments are defined by [x*(1-dx/(2*10^6))] and [x*(1+dx/(2*10^6))], respectively. For values of x = 2000 (m/z) and dx = 1000, the width of the | * dx (ppm): a parameter defining the width and the number of the m/z spectra segments. For example, a spectral segment centered at the position x covers a m/z interval of the width x * dx/10^6. The boundaries of the spectra segments are defined by [x*(1-dx/(2*10^6))] and [x*(1+dx/(2*10^6))], respectively. For values of x = 2000 (m/z) and dx = 1000 (ppm), the width of the respective segment is 2 and the m/z values of the boundaries are 1999 and 2001. | ||
* intensity: defines if barcode spectra or peak weighting factors are utilized as test inputs | * intensity: defines if barcode spectra (check box unchecked) or peak weighting factors (checked) are utilized as test inputs | ||
* show histogram: | * show histogram: opens a user dialog box with an histogram of the test outputs (p-values, t-values, etc.) and provides also the means, medians and the standard deviations of the test variables. | ||
== Performing | == Performing t-test series == | ||
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the [[Load spectra (Bruker format)|load spectra]] (Bruker data file format), [[Import Mass Spectra in a mzXML Data Format|import spectra from mzXML data]], or the ''load MS multifile'' options of the ''File'' | 1. Load the mass spectral data files via the [[Load spectra (Bruker format)|load spectra]] (Bruker data file format), [[Import Mass Spectra in a mzXML Data Format|import spectra from mzXML data]], or the ''load MS multifile'' options of the ''File'' pull down menu. | ||
2. Two-samples t-tests are carried out from labeled spectra, i.e. from spectra with a [[Class Assignment|class assignment]]. To perform the test label two groups of spectra as class 1 and as class 2, respectively. Labeling, or class assignment, can be carried out by selecting the appropriate spectra and choosing ''class assignments'' --> ''class X'' from the ''Edit'' | 2. Two-samples t-tests are carried out from labeled spectra, i.e. from spectra with a [[Class Assignment|class assignment]]. To perform the test label two groups of spectra as class 1 and as class 2, respectively. Labeling, or class assignment, can be carried out by selecting the appropriate spectra and choosing ''class assignments'' --> ''class X'' from the ''Edit'' pull down menu. | ||
3. The t-test routine always starts from original MALDI- | 3. The t-test routine always starts from original MALDI-ToF mass spectra, i.e. [[Spectral Pre-processing| spectral pre-processing]] and [[Peak Detection|peak detection]] is carried out automatically using pre-defined parameters. Existing pre-processed spectra and pre-defined peak tables are ignored by the test routine. | ||
4. Define test parameter, such as α (significance level), the m/z range and dx (''ppm'') which has a default value of 1000 (relative, in ppm). The parameter dx defines the width of m/z segments in which spectra are divided during the test. Peaks found in the same m/z segment are considered identical while mass peaks in different segments are considered different peaks. | 4. Define test parameter, such as α (significance level), the m/z range and dx (''ppm'') which has a default value of 1000 (relative, in ppm). The parameter dx defines the width of m/z segments in which spectra are divided during the test. Peaks found in the same m/z segment are considered identical while mass peaks in different segments are considered different peaks. | ||
5. When finished select ''t-test'' from the ''Analysis'' | 5. When finished select ''t-test'' from the ''Analysis'' pull down menu. Choose options ''plot decision for H(0)'', ''plot p-values'' or ''plot t-values'', to obtain the respective outputs of the t-tests. | ||
== Output of | == Output of the univariate t-test series == | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Example of the output from a serial t-test taken from the [[The Log-File (logfile.txt)|log file]] of MicrobeMS: | Example of the output from a serial t-test taken from the [[The Log-File (logfile.txt)|log file]] of MicrobeMS: | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
|[[File:t-test-cmdln-output.png|474px|thumb| | |[[File:t-test-cmdln-output.png|474px|thumb|Command line output of t-tests]] | ||
|[[File:T-test-plot.jpg|400px|thumb|p-values plot of univariate t-tests (log scaled) | |[[File:T-test-plot.jpg|400px|thumb|p-values plot of univariate t-tests (log scaled): The smaller the p-value at the specific m/z position the higher the discriminative potential of biomarker peaks at this position]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:15, 11 April 2025
Introduction
This function performs two-samples t-tests in each segment of the MALDI-ToF mass spectra using peak table data as inputs. t-tests are useful for biomarker screening in ensembles of mass spectra exhibiting certain degree of similarity. A two-samples t-test in a given m/z segment returns a test decision for the null hypothesis H(0) that the peak intensity data in class I and class II come from independent random samples from normal distributions with equal means and variances. The alternative hypothesis H(1) is that the peak intensity data come from populations with unequal means.
See also t-test (Wikipedia)
Parameter of the two-samples t-test
- m/z range: boundaries of the m/z region in which the t-tests are performed
- α: significance level of the t-tests
- dx (ppm): a parameter defining the width and the number of the m/z spectra segments. For example, a spectral segment centered at the position x covers a m/z interval of the width x * dx/10^6. The boundaries of the spectra segments are defined by [x*(1-dx/(2*10^6))] and [x*(1+dx/(2*10^6))], respectively. For values of x = 2000 (m/z) and dx = 1000 (ppm), the width of the respective segment is 2 and the m/z values of the boundaries are 1999 and 2001.
- intensity: defines if barcode spectra (check box unchecked) or peak weighting factors (checked) are utilized as test inputs
- show histogram: opens a user dialog box with an histogram of the test outputs (p-values, t-values, etc.) and provides also the means, medians and the standard deviations of the test variables.
Performing t-test series
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the load spectra (Bruker data file format), import spectra from mzXML data, or the load MS multifile options of the File pull down menu.
2. Two-samples t-tests are carried out from labeled spectra, i.e. from spectra with a class assignment. To perform the test label two groups of spectra as class 1 and as class 2, respectively. Labeling, or class assignment, can be carried out by selecting the appropriate spectra and choosing class assignments --> class X from the Edit pull down menu.
3. The t-test routine always starts from original MALDI-ToF mass spectra, i.e. spectral pre-processing and peak detection is carried out automatically using pre-defined parameters. Existing pre-processed spectra and pre-defined peak tables are ignored by the test routine.
4. Define test parameter, such as α (significance level), the m/z range and dx (ppm) which has a default value of 1000 (relative, in ppm). The parameter dx defines the width of m/z segments in which spectra are divided during the test. Peaks found in the same m/z segment are considered identical while mass peaks in different segments are considered different peaks.
5. When finished select t-test from the Analysis pull down menu. Choose options plot decision for H(0), plot p-values or plot t-values, to obtain the respective outputs of the t-tests.
Output of the univariate t-test series
Example of the output from a serial t-test taken from the log file of MicrobeMS: