Create database spectra: Difference between revisions
m (→Related topics) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Database spectra are the preferred type of database entries in MicrobeMS. Such database spectra constitute the spectral references of a microbial library. Ideally database spectra are obtained from multiple measurements of the bacterial isolate under study in order to cover the spectral variability contained in the spectra of biological and technical replicates. | Database spectra are the preferred type of database entries in MicrobeMS. Such database spectra constitute the spectral references of a microbial library. Ideally database spectra are obtained from multiple measurements of the bacterial isolate under study in order to cover the spectral variability contained in the spectra of biological and technical replicates. The number of individual spectra used for database spectrum generation should ideally vary between 12 and 20 and should include data from 3 biological and 4 technical replicates. | ||
The concept of database spectra involves automated generation of peak tables from spectral measurement series in which information about peak positions (m/z), normalized peak intensities and peak frequencies are obtained. | The concept of database spectra involves automated generation of peak tables from spectral measurement series in which information about peak positions (m/z), normalized peak intensities and peak frequencies are obtained. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Mass peak tables from unknown microbial strains are then compared by pattern matching algorithms against a library of database spectra. The results of the pattern matching analyses can be provided as a matching rank rank list, either in a text, or a HTML format. These reports are easy to interpret and allow microbial identification down to the species level. | Mass peak tables from unknown microbial strains are then compared by pattern matching algorithms against a library of database spectra. The results of the pattern matching analyses can be provided as a matching rank rank list, either in a text, or a HTML format. These reports are easy to interpret and allow microbial identification down to the species level. | ||
The database spectrum in the strict sense is represented by a simple average spectrum with a special type of peak table. Peak tables of database spectra contain the relevant information for the identification algorithms. Unlike the peak tables obtained from single experimental mass spectra the peak tables of database spectra contain also peak frequency information. | The database spectrum in the strict sense is represented by a simple average spectrum with a special type of peak table. Peak tables of database spectra contain the relevant information for the identification algorithms. Unlike the peak tables obtained from single experimental mass spectra the peak tables of database spectra contain also the peak frequency information. | ||
== Producing database spectra == | == Producing database spectra == | ||
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the [[Load spectra (Bruker format)|''load spectra'']] (Bruker data file format), [[Import Mass Spectra in a mzXML Data Format|''import spectra from mzXML data'']], or the ''load MS multifile'' options of the ''File'' pulldown menu. | |||
[[File:batch-dbspectra.jpg||right|Screenshot of the window ''create db spectra'']] | [[File:batch-dbspectra.jpg||right|Screenshot of the window ''create db spectra'']] | ||
2. To produce a database spectrum select the respective mass spectra in the listbox at the | 2. To produce a database spectrum select the respective mass spectra in the listbox at the top left corner (the listbox is labeled by ''MicrobeMS spectra ID`s''). To select multiple spectra hold the <Shift> key while selecting. | ||
3. Start the procedure by selecting ''create database spectra'' → ''from selection'' from | 3. Start the procedure by selecting ''create database spectra'' → ''from selection'' from the ''Analysis'' pull down menu. Database spectra can be also created from labeled spectra, i.e. from spectra with a [[Class Assignment|''class assignment'']]. Labeling, or class assignment, can be carried out by selecting the appropriate spectra and choosing ''class assignments'' → ''class X'' from the ''Edit'' pulldown menu. | ||
4. As a result database spectra are created from peak lists produced from series of pre-processed | 4. As a result database spectra are created from peak lists produced from series of pre-processed mass spectra. The parameters used for spectral pre-processing and peak detection are stored in the MicrobeMS configuration file [[Description of MicrobeMS' main parameter file 'microbems.opt'|''microbems.opt'']]. When the procedure is finished a window entitled ''view/edit metadata and pre-processing parameters'' comes up which offers the possibility to inspect and modify the metadata information. Furthermore, a new file ID in the format dbspec-DD-MON-YEAR-HR-MI-SE.XXX will be created and assigned. | ||
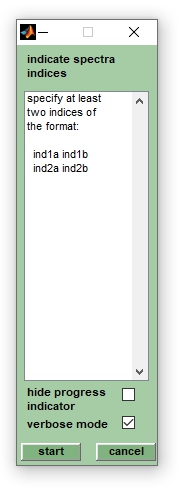
5. An option to create series of database spectra in an automated way is available from the | 5. An option to create series of database spectra in an automated way is available from the option ''create database spectra'' → ''db spec batch mode'' (''Analysis'' pull down menu). A window entitled ''create db spectra'' offers the possibility to indicate indices of the mass spectra to be used. For example, to create a database spectrum from spectra 1-8 and to create a second database spectrum from spectra 12-14 indicate 1 8 in the first line, and 12 14 in the second line. Press ''start'' when finished. | ||
== Related topics == | == Related topics == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 6 June 2025
Introduction
Database spectra are the preferred type of database entries in MicrobeMS. Such database spectra constitute the spectral references of a microbial library. Ideally database spectra are obtained from multiple measurements of the bacterial isolate under study in order to cover the spectral variability contained in the spectra of biological and technical replicates. The number of individual spectra used for database spectrum generation should ideally vary between 12 and 20 and should include data from 3 biological and 4 technical replicates.
The concept of database spectra involves automated generation of peak tables from spectral measurement series in which information about peak positions (m/z), normalized peak intensities and peak frequencies are obtained.
Mass peak tables from unknown microbial strains are then compared by pattern matching algorithms against a library of database spectra. The results of the pattern matching analyses can be provided as a matching rank rank list, either in a text, or a HTML format. These reports are easy to interpret and allow microbial identification down to the species level.
The database spectrum in the strict sense is represented by a simple average spectrum with a special type of peak table. Peak tables of database spectra contain the relevant information for the identification algorithms. Unlike the peak tables obtained from single experimental mass spectra the peak tables of database spectra contain also the peak frequency information.
Producing database spectra
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the load spectra (Bruker data file format), import spectra from mzXML data, or the load MS multifile options of the File pulldown menu.
2. To produce a database spectrum select the respective mass spectra in the listbox at the top left corner (the listbox is labeled by MicrobeMS spectra ID`s). To select multiple spectra hold the <Shift> key while selecting.
3. Start the procedure by selecting create database spectra → from selection from the Analysis pull down menu. Database spectra can be also created from labeled spectra, i.e. from spectra with a class assignment. Labeling, or class assignment, can be carried out by selecting the appropriate spectra and choosing class assignments → class X from the Edit pulldown menu.
4. As a result database spectra are created from peak lists produced from series of pre-processed mass spectra. The parameters used for spectral pre-processing and peak detection are stored in the MicrobeMS configuration file microbems.opt. When the procedure is finished a window entitled view/edit metadata and pre-processing parameters comes up which offers the possibility to inspect and modify the metadata information. Furthermore, a new file ID in the format dbspec-DD-MON-YEAR-HR-MI-SE.XXX will be created and assigned.
5. An option to create series of database spectra in an automated way is available from the option create database spectra → db spec batch mode (Analysis pull down menu). A window entitled create db spectra offers the possibility to indicate indices of the mass spectra to be used. For example, to create a database spectrum from spectra 1-8 and to create a second database spectrum from spectra 12-14 indicate 1 8 in the first line, and 12 14 in the second line. Press start when finished.